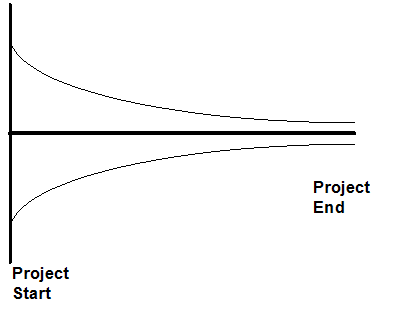
| Region of Uncertainty is large at project start.
Actual schedule becomes better known as the project unfolds.
Goal - Minimize magnitude of the uncertainty at project start.
Update estimates throughout project.
Without a schedule estimation method, expect the initial estimate to be off by as much as 400%
Estimation methods (in order of effectiveness) include: |
 |
#1 Bottom-Up
- Identify functional characteristics of the system.
- Estimate effort to create the functionality.
- Total the effort to arrive at the completion date.
- Uses formal methods such as Function Point Analysis and/or COnstructive COst MOdel (COCOMO).
#2 Analogy
- Project is similar to previous projects.
- Requires keeping project history data so that future projects can benefit from metrics.
#3 Top-Down
- Decomposition of tasks into subtasks.
- Estimate the time required for each subtask.
- Some tasks may be concurrent, or may be dependant on other tasks.
- Total the time to get the completion date.
- MS Project encourages this approach.
|
#4 Price-to-Win
- Low-ball bid to win contract.
- May result in unacceptable tradeoffs between cost, schedule, and quality.
- Generally results in long, uncompensated overtime hours.
#5 Dictated by Circumstances
- External forces may dictate the cost, schedule, or quality.
- Requires high degree of flexibility in the non-dictated factors.
- Must verify that the dictated circumstances are real and not imaginary.
#6 Guess
- Scratch head and pull out dates. “I think it will take, hmmmm, 2 weeks.”
- According to IBM studies, guesses are typically off target by 200% to 400%..
- Indicative of companies that use project planning tools, but do not have the methodologies or mindset
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT).
- Weighted average approach improves quality of estimate.
- Can be used in conjunction with any approach except Dictated by Circumstances.
- Obtain three estimates for each task: the most optimistic, the most likely, and the most pessimistic.
Time = Optimistic + 4xMostLikely + Pessimistic
6 |